Comment traiter l’hernie discale?
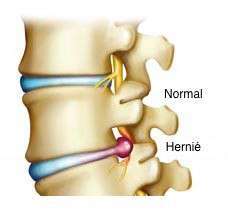
A herniated disc is a protrusion or small bump at the level of the portion of an intervertebral disc, compressing a nerve root or the spinal cord. This compression is the cause of the pain. Indeed, the intervertebral disc is composed of a solid and fibrous structure with a gelatinous nucleus, also called nucleus pulposus. The role of the disc is to bring flexibility to the spine and to absorb the shocks linked to bad movements. In the event of a herniated disc, this disc can then tear or be ruptured. Herniated Disc Symptom Treatment
Lumbar disc herniation: the most common herniation
Although a herniated disc can affect any region of the spine, the vast majority of herniated discs occur in the lower back, in the lumbar region. In this case, the hernia can cause low back pain.
If the hernia compresses one of the roots of the sciatic nerve, it can be accompanied by pain along one leg: this is sciatica. A hernia can also go unnoticed; this is usually the case when it does not compress a nerve root.
The causes of a herniated disc
The causes of a herniated disc are multiple and, most often, several of these causes must be combined for it to appear:
- dryness of the intervertebral disc , most often due to age, and sometimes aggravated by poor hydration of the body (for example during hot weather);
- wear and tear on the intervertebral disc due to repeated exertion, poor posture, prolonged sitting day after day, etc. An area of the disc is then subjected to intense and repeated pressure, which weakens it.
- a family background that makes the intervertebral discs more vulnerable, due to their morphology or poor posture of the spine.
- trauma that damages the disc or suddenly subjects it to very intense pressure.
Contrary to popular misconception, stress and anxiety cannot cause a herniated disc . However, they can contribute to maintaining the problem and making it a chronic disease. Herniated Disc Symptom Treatment
What are the symptoms of herniated disc?
Compression of the disc on the nerve roots is the cause of different symptoms: sciatica when it comes to the root at the lumbar level and cervico-brachialgia , which is rarer, when the hernia is cervical.
In addition to these two well-known symptoms of herniated disc, many others exist (non-exhaustive list):
- pain in the limbs. The course of the pain depends on the root compressed by the hernia;
- tingling or prickling sensations (paraesthesia), disturbance of sensitivity (dysesthesia) which may go as far as complete loss of sensitivity (anaesthesia). The affected area depends on the affected root;
- partial or complete loss of muscle strength is also possible;
- sphincter disorders are rare but possible in certain herniated discs;
The pressure of the herniated disc on the root is most often manifested by pain.
Complication
Although painful, herniated discs rarely cause complications . The compressed nerve fibers, when they are sensitive (those that transmit touch and pain), recover well from the compression once the disc is back in place.
However, in some cases (see box below), the hernia compresses the nerve fibers that control the muscles (the “motor” fibers). These recover poorly from compression, which can lead to lasting paralysis . In this case, the compression must be lifted as quickly as possible, through urgent surgery.
A sudden decrease or disappearance of pain due to a herniated disc may be a sign of worsening nerve compression and motor fiber damage. In addition, weakness in an arm or leg, or the inability to walk on tiptoes or heels may indicate damage to the motor fibers that innervate the leg. At the level of the arm, the compression of the motor fibers can result in a loss of dexterity of the fingers. Herniated Disc Symptom Treatment
How to treat and cure a herniated disc? Treatment
If you suffer from very acute pain, it is recommended to avoid major efforts. If necessary, speak with your doctor and pharmacist for pain management with the medication best suited to your condition, especially if your sleep is affected.
Follow-up in physiotherapy or occupational therapy is very effective in managing pain. It will also help you get back to work faster.
Even if the pain is severe, you can start your physiotherapy treatments. You will be taught exercises to manage pain and help regain your mobility.
Gradually resuming activities such as walking, core-strengthening exercises, and some temporary changes in transfer technique will promote healing.
Teaching better work methods when moving loads will reduce the risk of a recurrence.
During treatments, your physiotherapist may use different treatment approaches, including tissue and muscle loosening techniques, manual therapy, pull-ups and mobilizations.
These techniques are intended to help you relieve symptoms and thereby help you move more easily.
An interesting and positive fact is that research tends to show that a hernia can heal naturally with conservative treatments. Moreover, the larger it is, the greater its percentage of regression!
A LIRE:
Commentaires récents